生化分析试剂 Biochemical Assay Reagents
PEG300;(Synonyms: 聚乙二醇; Polyethylene glycol 300)
PEG300 (Polyethylene glycol 300),分子量为300的中性聚合物,由乙二醇重复单元形成的水溶性、低免疫原性和生物相容性聚合物。
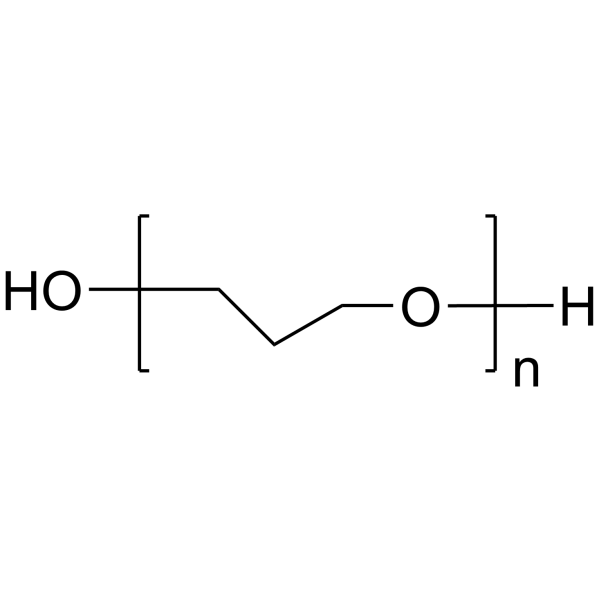
PEG300 Chemical Structure
CAS No. : 25322-68-3
| 规格 | 价格 | 是否有货 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mL | ¥350 | In-stock | |
| 100 mL | ¥450 | In-stock | |
| 200 mL | ¥765 | In-stock | |
| 500 mL | ; | 询价 | ; |
| 1L | ; | 询价 | ; |
* Please select Quantity before adding items.
| 生物活性 |
PEG300 (Polyethylene glycol 300), a neutral polymer of molecular weight 300, is a water-soluble, low immunogenic and biocompatible polymer formed by repeating units of ethylene glycol[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
The FDA has approved polyethylene glycol (PEG) for use as a vehicle or base in foods, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, including injectable, topical, rectal and nasal formulations. PEG shows little toxicity, and is eliminated from the body intact by either the kidneys (for PEGs < 30 kDa) or in the faeces (for PEGs > 20 kDa). PEG lacks immunogenicity, and antibodies to PEG are generated in rabbits only if PEG is combined with highly immunogenic proteins[3]. MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Guidelines (Following is our recommended protocol. This protocol only provides a guideline, and should be modified according to your specific needs). MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
| 分子量 |
300.00 |
| CAS 号 |
25322-68-3 |
| 中文名称 |
聚乙二醇 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
| 储存方式 |
4deg;C, sealed storage, away from moisture |
| 溶解性数据 |
In Vitro:;
DMSO : 100 mg/mL (333.33 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : ≥ 50 mg/mL (166.67 mM) * “≥” means soluble, but saturation unknown. |
| 参考文献 |
|
