天然产物 糖类和糖苷 Saccharides and Glycosides
Hyaluronic acid;(Synonyms: 玻尿酸; Hyaluronate)
Hyaluronic acid (来自玉米发酵) 是由二糖的重复单元组成的生物聚合物,应用领域广泛。
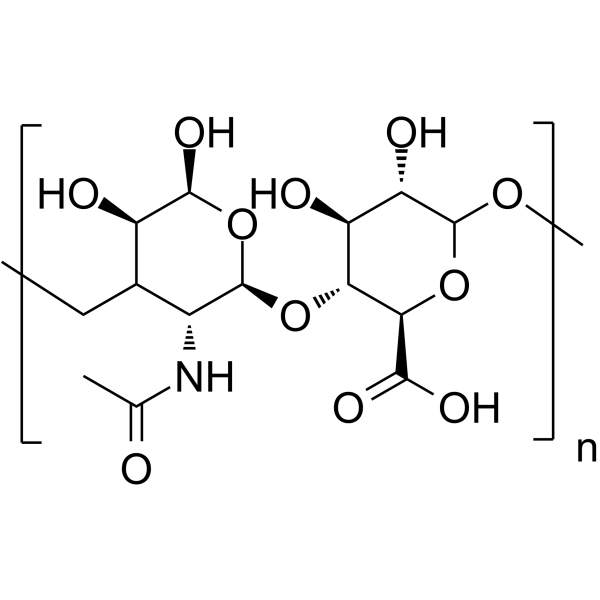
Hyaluronic acid Chemical Structure
CAS No. : 9004-61-9
| 规格 | 价格 | 是否有货 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Sample (0.1-0.5 mg) | ; | Apply now | ; |
| 50 mg | ¥500 | In-stock | |
| 100 mg | ¥700 | In-stock | |
| 200 mg | ¥900 | In-stock | |
| 500 mg | ¥1500 | In-stock | |
| 1 g | ¥1900 | In-stock | |
| 5 g | ; | 询价 | ; |
| 10 g | ; | 询价 | ; |
* Please select Quantity before adding items.
Hyaluronic acid 相关产品
bull;相关化合物库:
- Natural Product Library Plus
- Drug Repurposing Compound Library Plus
- FDA-Approved Drug Library Plus
- Bioactive Compound Library Plus
- Metabolism/Protease Compound Library
- Natural Product Library
- FDA-Approved Drug Library
- Anti-Cancer Compound Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Drug Repurposing Compound Library
- Anti-COVID-19 Compound Library
- NMPA-Approved Drug Library
- Orally Active Compound Library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Monomer Library
- FDA Approved amp; Pharmacopeial Drug Library
- Food-Sourced Compound Library
- Inactive Ingredient Library
- Rare Diseases Drug Library
- Childrenrsquo;s Drug Library
| 生物活性 |
Hyaluronic acid (corn fermented) is a biopolymer composed of repeating units of disaccharides with various applications. |
|
|---|---|---|
| IC50 Target |
|
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is widely used in aesthetic medicine due to its binding ability with a large number of water molecules. It improves tissue hydration and their resistance to mechanical damage. HA plays an important role in wound healing, ovulation, fertilization, signal transduction, and tumor physiology. HA is used in joint diseases such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. HA of a high molecular mass reduces the chemotaxis and migration of inflammatory cells which acts as a good barrier to the inflammatory process and protects against the effects of free radicals. HA is used in ophthalmology due to its lubricating properties for the corneal endothelium, and improves tissue hydration and cellular resistance to mechanical damage in aesthetic dermatology, and has marginal adverse effects. Several trials indicate its role in tumor markers, liver diseases, and in pharmaceuticals[1]. Hyaluronan plays an important role in cancer growth and metastasis. HA and HA fragment-tumor cell interaction could activate the downstream signaling pathways, promoting cell proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion, and inducing angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stem cell-like property, and chemoradioresistance in digestive cancers[2]. MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
The impact of applied intra-articular HA has been proven in many studies in animals. Studies on HA have shown that it promotes the synthesis of cartilage matrix, prevents its degradation, reduces inflammation, stimulates the synthesis of endogenous HA, and improves the resilience and moisture of cartilage [1]. High molecular size HA preparations, applied topically, promote healing of fresh skin wounds. They also promote the healing of venous leg ulcers and are useful in the management of chronic wounds[3]. MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
|
| Clinical Trial |
|
|
| 分子量 |
379.32 (monomer) |
|
| Formula |
C16H27NO11 |
|
| CAS 号 |
9004-61-9 |
|
| 中文名称 |
玻尿酸;透明质酸;玻璃酸 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
|
| 储存方式 |
4deg;C, protect from light *In solvent : -80deg;C, 6 months; -20deg;C, 1 month (protect from light) |
|
| 溶解性数据 |
In Vitro:;
H2O : 14.29 mg/mL (Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 1 mg/mL (ultrasonic and warming and heat to 80°C) |
|
| 参考文献 |
|
