天然产物 糖类和糖苷 Saccharides and Glycosides
Isovitexin 2”-O-arabinoside;(Synonyms: 异牡荆素-2”-O-阿拉伯糖苷) 纯度: 99.49%
Isovitexin 2”-O-arabinoside 是 Avena sativa L. 幼苗中的一种非活性类黄酮。
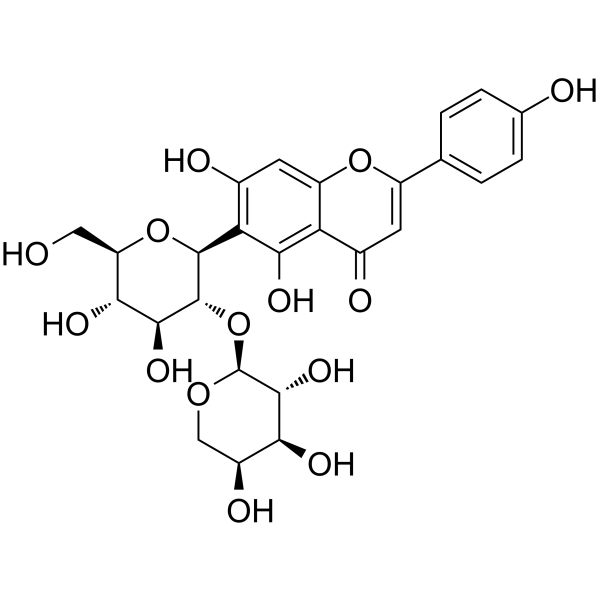
Isovitexin 2”-O-arabinoside Chemical Structure
CAS No. : 53382-71-1
| 规格 | 价格 | 是否有货 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | ¥4000 | In-stock | |
| 10 mg | ; | 询价 | ; |
| 50 mg | ; | 询价 | ; |
* Please select Quantity before adding items.
Isovitexin 2”-O-arabinoside 相关产品
bull;相关化合物库:
- Natural Product Library Plus
- Bioactive Compound Library Plus
- Natural Product Library
- Glycoside Compound Library
- Phenols Library
- Food-Sourced Compound Library
| 生物活性 |
Isovitexin 2”-O-arabinoside is an inactive flavonoid in plantlets of Avena sativa L. (Poaceae)[1]. |
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
564.49 |
| Formula |
C26H28O14 |
| CAS 号 |
53382-71-1 |
| 中文名称 |
异牡荆素-2”-O-阿拉伯糖苷 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
| 储存方式 |
4deg;C, sealed storage, away from moisture and light *In solvent : -80deg;C, 6 months; -20deg;C, 1 month (sealed storage, away from moisture and light) |
| 参考文献 |
|